In4Mo. Advanced System of Information on the Mobility of People and Vehicles
- AMPL, C++, CPLEX, Dynameq Simulator, Hibernate, HTML, Java, JBoss, JPA, JQuery, Matlab, PostGIS, PostgreSQL, R, Simulador Aimsun
Home » Success Stories »
Description
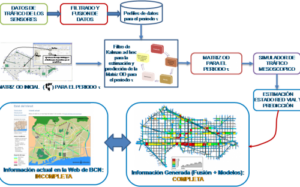
The main objective of the In4Mo project has been the development of applications that constitute the core of Smart Mobility, one of the fundamental pillars of the Smart City concept: the provision of information for traffic information systems, in any of their forms, and especially that of personal journey planners and Active Traffic Management systems, which allow the person responsible for managing the road network to have an adequate vision and estimate of the state of the road network and its plausible evolution in the short term, in order to make more efficient decisions.
In4Mo has been designing and developing according to foreseeable technological scenarios in the short-medium term, where traditional traffic detection technologies (e.g. magnetic induction loops) coexist with emerging technologies (e.g. magnetometers), among which ICT (Bluetooth, GPS…) play a relevant role, the penetrations and penetration trends of which allow relying on them in order to develop more efficient systems.
The fundamental thesis of In4Mo is that technology, i.e. sensorisation of the city, is a necessary but not sufficient condition for the generation of reliable, timely and value-added information, i.e. available where and when it is needed, in other words, that the degree of smartness is the result of efficient combination of data and its processing.
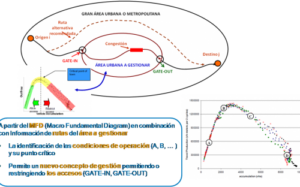
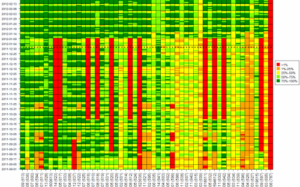
But the data provided by sensor measurements from different technologies are heterogeneous, so In4Mo’s primary innovative activity has been the proposal of a methodology for Data Filtering, Fusion and Completeness that incorporates and integrates a variety of flexible and efficient analysis and processing methods, constituting a product that underpins a basic platform for the provision of homogeneous and consistent data that feeds the models for traffic information and management from any control centre:
- Filtering techniques (non-linear, Kalman Filter…) that generate complete, consistent and robust sequences by elimination of outliers and completeness of missing data to generate complete series.
- Fusion techniques (Bayesian, neural networks, traffic models, etc.) that allow data from heterogeneous sources to be combined in a coherent manner to generate homogeneous information of higher quality than that of each of them individually.
- State estimation (state estimation models) and prediction techniques that allow an estimation of the state of the traffic system and the prognosis of its plausible evolution in a short-term time horizon.
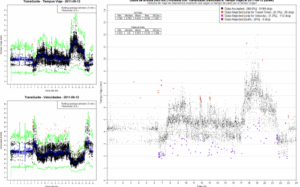
The availability of traffic data from ICT sensors allows for a substantial improvement in the quality of traffic information generated by currently operational systems; however, it will still take some time before the penetration of ICT technologies is sufficient to provide by itself a complete picture of traffic conditions on the entire road network, in particular in medium to large urban areas. Especially when the applications to be supported by the information system require real-time computation of paths between any origin-destination pairs as in the case of full navigation systems, or trip planning systems that do not have to be restricted to predetermined sets of paths (however important they may be). Consequently, the generation of complete and consistent information requires the use of dynamic traffic models that allow a global estimation of the state of the road network and predict its evolution in the short term in the absence of incidents. In4Mo has proposed two complementary dynamic traffic models:
- Models for the estimation of time-dependent Origin-Destination (OD) Matrices, based on the exploitation of traffic variable measures provided by ICT applications, by means of ad hoc versions of Kalman Filters.
- Models describing the dynamics of the propagation of traffic flows through the road network as a function of the temporal patterns of demand defined by the time-dependent OD matrices.
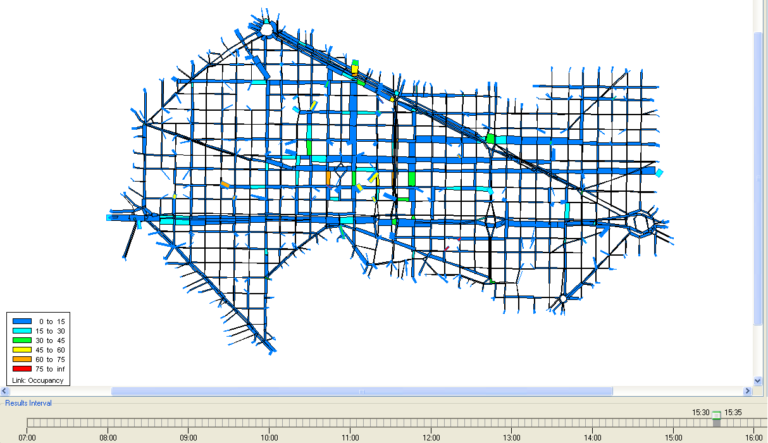
The realization that the same information generated by the combination of merged data and traffic models is what the traffic manager needs to manage a road network has been translated in In4Mo into an innovative proposal for Smart Mobility: active management based on the Macro Fundamental Diagram (MFD).
This project is part of the program Acción Estratégica de Telecomunicaciones y Sociedad de la Información, 2010. Subprograma: Avanza Competitividad I+D+I, (2010-2012).
Articles and presentations
J.Barceló, F. Gilliéron, M.P. Linares, O. Serch, L.Montero, The detection layout problem. Paper 12-2056, accepted for publication in Transportation Research Records: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, to appear in 2012.
J.Barceló, L.Montero, M.Bullejos, O. Serch and C. Carmona, A Kalman Filter Approach for the Estimation of Time Dependent OD Matrices Exploiting Bluetooth Traffic Data Collection, Paper #12-3843, presented at the 91st TRB Annual Meeting, January 2012, included in the Compendium of Papers.
J.Barceló, L.Montero, L. Marqués and C. Carmona, Travel time forecasting and dynamic of estimation in freeways based on Bluetooth traffic monitoring, Transportation Research Records: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, Vol. 2175 (2010), pp. 19-27
Un equip de la UPC desenvolupa un sistema per una millor gestió de la mobilitat, xip/tx, 30 abril 2013