Now that we are at the end of June and we have begun to work on preparing the laboratories for the next academic year, we want to show you how we manage the operating system installations in the FIB PC labs / classrooms.
Now that we are at the end of June and we have begun to work on preparing the laboratories for the next academic year, we want to show you how we manage the operating system installations in the FIB PC labs / classrooms.
It is clear that when you have to manage a computer park of more than 350 PCs, you have to rely on some tool that allows you to make a master image of a computer and distribute it in some way in the rest of equipments.
It becomes more complicated when we add different variables or requirements, such as:
- Different hardware, not all equipments are the same, since they were bought or renewed in different years.
- You work with more than one operating system natively, not virtualized (Windows and different versions of Linux)
- Cloning must be done by network, by groups of PCs and must be fast, it is not feasible to do it physically passing equipment to computer.
- You must be able to do post-configuration of systems once they are installed.
While it is true that there are some tools in the market that meet the conditions of the previous points, there are not so many if we want a free software tool and also free.
At this point, after evaluating several options, we decided to use the OpenGnSys tool, since in addition to satisfying all the requirements, it presents the following advantages:
- Cloning of Windows operating systems without having to resort to the sysprep utility of Microsoft, which greatly simplifies the creation of a master image of Windows.
- Post Configuring Windows and Linux systems using “scripts” in Bash Shell.
- Distribution of images using Unicast, Multicast or BitTorrent protocols. These last two are especially interesting when we have to do the distribution to many teams at once.
- Modular and scalable.
- Allows delegated administration.
- Focused in the educational field, although it can be applied in any other, it is a project created with the effort and collaboration of several universities of the state.
- It is a project that is alive and in constant evolution.
The technologies used by OpenGnSys are:
- LAMP Platform
- TFTP/PXE
- Samba/NFS
- Partclone
- Udpcast (multicast) i Bittornado (torrent)
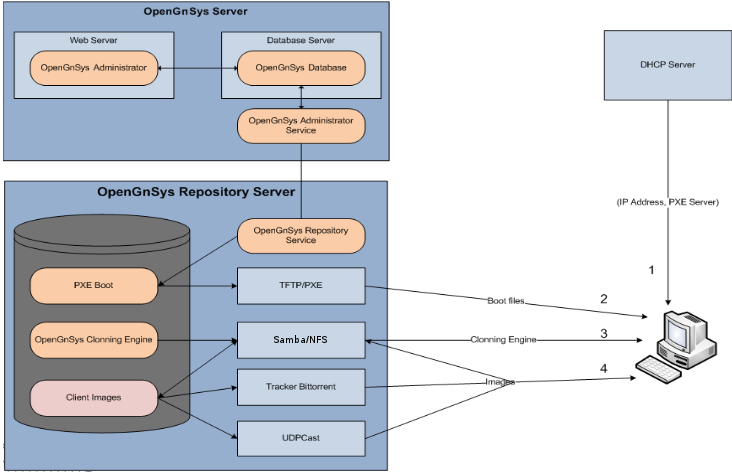 Graphic obtained from the project website http://www.opengnsys.es/wiki/DocumentacionUsuario1.0.6/Introduccion
Graphic obtained from the project website http://www.opengnsys.es/wiki/DocumentacionUsuario1.0.6/IntroduccionHow it works
The client computers boot from the network (the network card must support the PXE protocol, nowadays almost all have it), ask the DHCP server the IP that the computer has and the PXE server.Then the client will receive a “boot file” from the PXE server and then load the cloning engine, which is no more than a Linux mini-distribution that will wait for the commands sent to it from the OpenGnSYS server. These orders, among others, could be:
- Boot the operating system of a partition.
- Create a master image of a computer partition and save it to the server.
- Restore an image of an operating system from the server to the client.
- Show a menu to the user to choose which system to start.
Note that in installations that are not very large, a single Linux server can assume all the roles of an OpenGnSys server and, if necessary, this can be a virtual server without any problems.
The management of the environment is done via web and once we validate, we can create organizational units (for example schools), which will be formed by groups of classrooms and equipment.
From the same web environment we can create an image of a computer, restore an image to a computer for unicast, a whole classroom by multicast or bittorrent, partition all computers in a classroom or execute post-configuration scripts on a computer or every equipment of a classroom.
In short, a very powerful tool that can be used in any area where there is need to distribute images of operating systems.
The project website is www.opengnsys.es and if you decide to cooperate surely you would be welcome.